What Are the Possible Complications of Type 2 Diabetes, and How Can You Avoid Them?

If you have type 2 diabetes, you already know that smart medication, diet, and lifestyle choices can help you maintain healthy blood sugar levels and enjoy an excellent quality of life.
But in some cases, despite your best efforts to manage the disease, issues can arise.
Warding off the serious and sometimes fatal health complications linked with type 2 diabetes starts with being aware of their potential to affect you. Then, it’s important to take steps to decrease the risk of developing them.
5 Ways To Lower Your Risk Of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Next up video playing in 10 seconds
What Causes Health Complications of Diabetes?
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Complications
To avoid complications of type 2 diabetes, it’s imperative that you take care of yourself and keep your blood sugar under control.
It’s also important to maintain a healthy weight and good cholesterol levels.
How Common Are Diabetes Complications?
Side effects or complications of diabetes can be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic). Short-term means the problem can develop quickly at any time, and long-term means the problem generally develops later or more slowly over a period of time.
Possible Short-Term Complications of Diabetes
Sexual Issues
Diabetic Coma
Even though diabetic comas are rare, there’s the risk of unconsciousness with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood sugar).
Hypoglycemia can arise from excessive insulin, typically from drugs such as sulfonylureas or insulin. Unconsciousness happens when your brain doesn’t receive a sufficient amount of glucose to function properly. Early warning signs of hypoglycemia include hunger, sweating, and shaking.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diarrhea From Medication Use
Possible Long-Term Complications of Diabetes
Diabetic Neuropathy and Amputation
Eye Problems
Heart Disease and Stroke
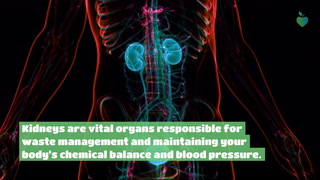
Kidney Disease
Sleep Apnea
Diabetic Dermopathy
This condition is harmless, and the skin patches don’t usually hurt or itch. Treatment isn’t necessary, and spots may disappear on their own.
Gum Disease
Cancer
How to Prevent Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes is unpredictable, but you can take steps to prevent complications. More than anything else, make sure your diabetes is well controlled. This includes taking diabetes medication as prescribed and never skipping a dose.
Also, learn how to recognize signs that your diabetes therapy isn’t working, and then speak with your doctor before complications arise. These signs include increased hunger, increased urination, fatigue, blurry vision, and headaches.
- Lose weight.
- Eat a balanced, healthy diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean meats.
- Monitor your intake of carbohydrates and sugary foods.
- Manage your cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Check your blood sugar level frequently when sick.
- Get seven to nine hours of sleep.
- Don’t smoke.
- Get annual physicals, vaccines, and eye examinations.
- Drink alcohol in moderation.
- Manage stress (stress hormones can increase insulin resistance).
How Doctors Diagnose Diabetes Complications
Blood Sugar Testing This test evaluates the amount of sugar in your bloodstream and can help your doctor determine whether your current diabetes treatment is working.
Retina Exam Eyedrops are used to dilate or widen your pupils, and then your doctor uses a machine to take a picture of your retina. This test assesses the health of your eyes and can help diagnose diabetic retinopathy.
Foot Examination Your doctor examines your feet for signs of infection, nerve damage, and poor circulation.
Cholesterol and Blood Screening Your doctor will draw a blood sample to check your cholesterol and also test to see if your blood pressure is within a healthy range. High blood pressure and cholesterol increase the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, stroke, and vision problems.
Kidney Screening You’ll provide a urine sample to see if there’s protein in your urine. Protein can be a sign of kidney damage.
Treatment for Diabetes Complications
Doctors will come up with a treatment plan after determining the severity of the condition.
Summary
Type 2 diabetes isn’t a disease to be taken lightly. So it’s important to take your medication as prescribed and to be open and honest with your doctor. Don’t ignore unusual symptoms of diabetes. These could indicate that your current therapy is no longer working, which puts you at risk for potentially serious complications.
Editorial Sources and Fact-Checking
Everyday Health follows strict sourcing guidelines to ensure the accuracy of its content, outlined in our editorial policy. We use only trustworthy sources, including peer-reviewed studies, board-certified medical experts, patients with lived experience, and information from top institutions.
Sources
- Insulin Resistance and Prediabetes. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Hyperglycemia in Diabetes: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Diabetes Care: 10 Ways to Avoid Complications. Mayo Clinic.
- It’s a Great Time to Get Moving. American Diabetes Association.
- Prediabetes — Your Chance to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- GP Based Weight Loss Programme Can Reverse Type 2 Diabetes. BMJ.
- What Affects Blood Sugar Levels. Diabetes.co.uk.
- Diabetes: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Diabetes, Sexual, and Bladder Problems. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Diabetic Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome. MedlinePlus.
- Diabetic Coma: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Diabetes and DKA (Ketoacidosis). American Diabetes Association.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Managing Sick Days. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Metformin (Oral Route). Mayo Clinic.
- Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. The Review of Diabetic Studies.
- Diabetic Neuropathy. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Diabetic Retinopathy. National Eye Institute.
- Diabetes, Heart Disease, and Stroke. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Diabetes and Heart Disease. Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- Diabetic Nephropathy (Kidney Disease): Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Sleep Apnea: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Can Long-term Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With CPAP Improve Glycemia and Prevent Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes Care.
- Diabetes and Skin Complications. American Diabetes Association.
- Diabetes and Dental Health. MouthHealthy.
- Gum Disease. Diabetes.co.uk.
- Gum Disease and Other Diseases. American Academy of Periodontology.
- Diabetes and Cancer: What’s the Link? National Foundation for Cancer Research.
- A1C Test: About. Mayo Clinic.
- Diabetes. Cleveland Clinic.
- Screening for Diabetes Complications. Diabetes.co.uk.
- Insulin Routines. American Diabetes Association.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clinic.
Resources
- Insulin Resistance and Prediabetes. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. May 2018.
- Hyperglycemia in Diabetes: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. August 20, 2022.
- Diabetes Care: 10 Ways to Avoid Complications. Mayo Clinic. January 29, 2022.
- It’s a Great Time to Get Moving. American Diabetes Association.
- Prediabetes — Your Chance to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. December 30, 2022.
- Kmietowicz Z. GP Based Weight Loss Programme Can Reverse Type 2 Diabetes. BMJ. December 5, 2017.
- What Affects Blood Sugar Levels. Diabetes.co.uk. January 25, 2023.
- Diabetes: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. January 20, 2023.
- Diabetes, Sexual, and Bladder Problems. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. June 2018.
- Diabetic Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome. MedlinePlus. January 9, 2022.
- Diabetic Coma: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. August 11, 2022.
- Diabetes and DKA (Ketoacidosis). American Diabetes Association.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. October 6, 2022.
- Managing Sick Days. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. February 28, 2022.
- Metformin (Oral Route). Mayo Clinic. March 1, 2023.
- Filippatos TD, Panagiotopoulou TV, Elisaf MS. Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. The Review of Diabetic Studies. Fall–Winter 2014.
- Diabetic Neuropathy. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Diabetic Nephropathy (Kidney Disease): Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. October 19, 2021.
- Diabetic Retinopathy. National Eye Institute. July 8, 2022.
- Diabetes, Heart Disease, and Stroke. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. April 2021.
- Diabetes and Heart Disease. Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- Sleep Apnea: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. December 23, 2022.
- Reutrakul S, Mokhlesi B. Can Long-Term Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With CPAP Improve Glycemia and Prevent Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes Care. August 2020.
- Diabetes and Skin Complications. American Diabetes Association.
- Gum Disease and Other Diseases. American Academy of Periodontology.
- Diabetes and Cancer: What’s the Link? National Foundation for Cancer Research. October 28, 2020.
- A1C Test: About. Mayo Clinic. December 1, 2022.
- Diabetes. Cleveland Clinic. February 17, 2023.
- Screening for Diabetes Complications. Diabetes.co.uk. January 25, 2023.
- Insulin Routines. American Diabetes Association.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clinic. September 3, 2021.
- Diabetes and Dental Health. MouthHealthy.
- Gum Disease. Diabetes.co.uk. January 25, 2023.



